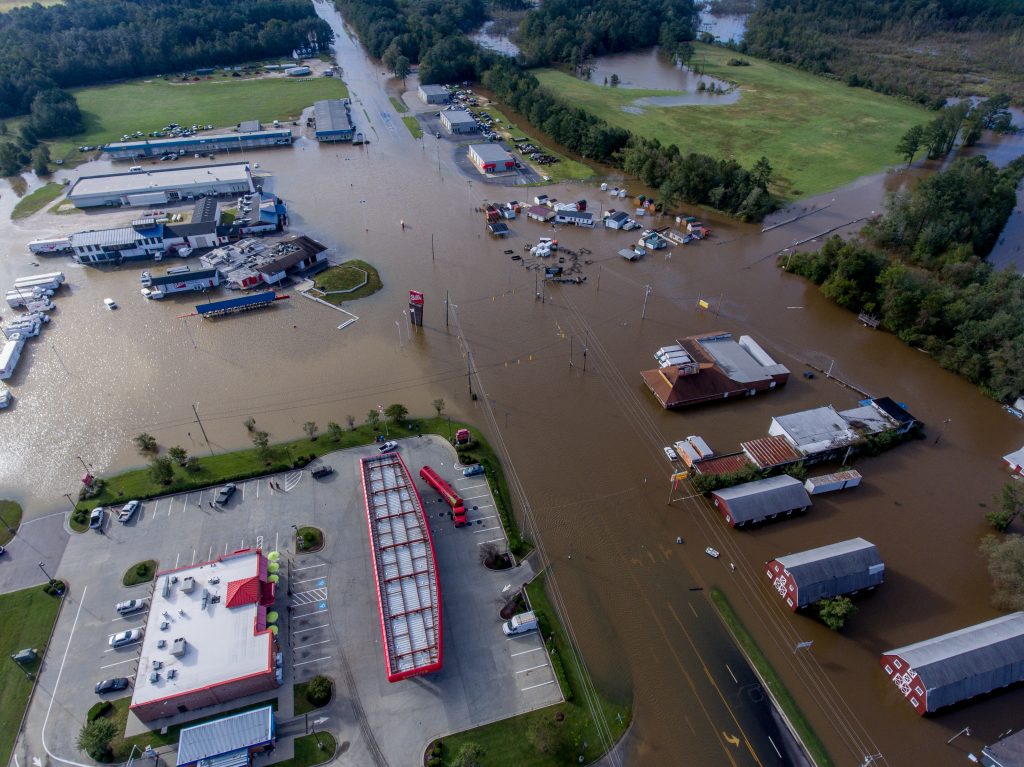
Case Study: North Carolina’s Journey to Flood Resilience
How a state plan and budget are enabling conditions for the development of nature-based methods. After frequent, disastrous storms and a state largely in need of repair, Governor Roy Cooper signed Executive Order 801 in October 2018, which is North Carolina’s commitment to address climate change and transition to a clean energy economy. This order…
Read MoreBogota Urban Land Use Management and Flood Risk Reduction
Colombia’s capital, Bogotá, has a population of 9 million people and is the center of the country’s administrative, financial, cultural and service life. Bogotá is located on a savanna, 2,600 meters above sea level, on the eastern Andean mountain range. The city is crossed by rivers and surrounded by wetlands and mountains. Despite its growing…
Read MoreMeeting Multiple Objectives with Flood Risk Management
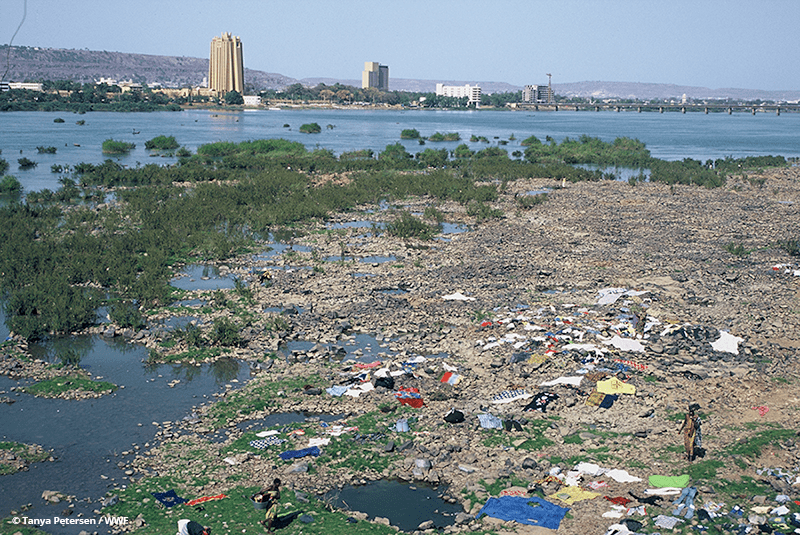
Water and sanitation are intrinsically linked to flood risk management, particularly in urban areas. When sewage and drainage infrastructure is unable to keep up with population growth, flood risk is increased; flood risk can also be compounded when outflows, drains and waterways are blocked by debris or encroached upon or occupied by informal settlements. Such a situation…
Read MoreFlash Floods: Alternative Management Options in Kulob City, Tajikistan
The city of Kulob, located in south-center Tajikistan, is an area extremely vulnerable to flash flooding. Typically, between March and May, a combination of heavy rainfall and snow melt flow into normally dry rivers and gullies. Paved streets, dense housing, and the growth of urban areas into the hills above the city make flash flood…
Read MoreFactors in Urban Flooding
Urban flooding typically results from multiple factors at multiple scales. Changes to land use upstream or in the region, or other factors within city limits, can lead to local flooding. The case below illustrates how urban flooding can be managed at different scales. In 1998, intense rainfall led to a severe flood and inundation of…
Read MoreLooking Upstream to Manage Flood Risk: A Pakistan Example
An integrated watershed approach to flood risk management addresses flood risk holistically and can lead to positive outcomes across multiple sectors. The Ayubia National Park (ANP) covers over 7,000 acres (3,000 hectares) in the Galliat region in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, a northwestern province of Pakistan, and is located within the moist temperate zone of the Himalayan-Karakoram-Hindu…
Read MoreThe Role of Gaming in Water Resource Management
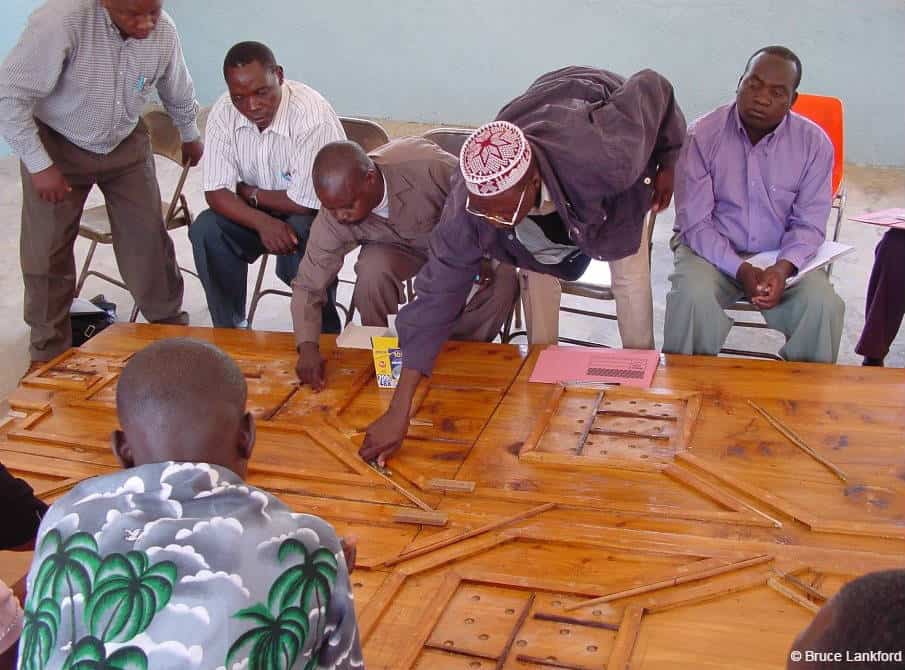
Bruce Lankford at the University of East Anglia in the United Kingdom developed the River Basin Game in 2000 to teach his students about management of shared resources. Dr. Lankford has since traveled to Tanzania, Malawi, Nigeria, South Africa and India and uses the game to engage community water users and municipal officials in the…
Read MoreVoices of Youth Mapping Risk Around the Globe
While some mapping is conducted by professionals with sophisticated technical equipment, UNICEF has instead targeted youths as experts in mapping social and environmental risks in communities around the world.[1] The goal behind this initiative is to enhance community engagement and participatory planning to more effectively reduce risk in vulnerable communities. The process starts with youth playing…
Read MoreEmploying Community Participation and Technology to Reduce Flood Risk in the Bicol River Basin
The Bicol River Basin (BRB), located in the southern portion of Luzon Island, Philippines, receives at least 2,000 mm of rainfall per year, primarily during typhoon season, and experiences regular flooding. In 2008, Christian Aid launched a pilot project, Reduction of Flood Risk in the Bicol River Basin II (BRB2), as a part of their…
Read MoreEcosystem Service Multiple Benefits: A Belize Example
Placencia Peninsula in Stann Creek District, Belize, is a 16-mile-long ribbon of land with the Caribbean Sea to its east and the Placencia Lagoon to its west. The ecosystems of the peninsula and lagoon include coarse sands, littoral forest, mangroves and wetlands.Village expansion and tourism development have led to drastic reduction of local mangrove systems. Development…
Read More